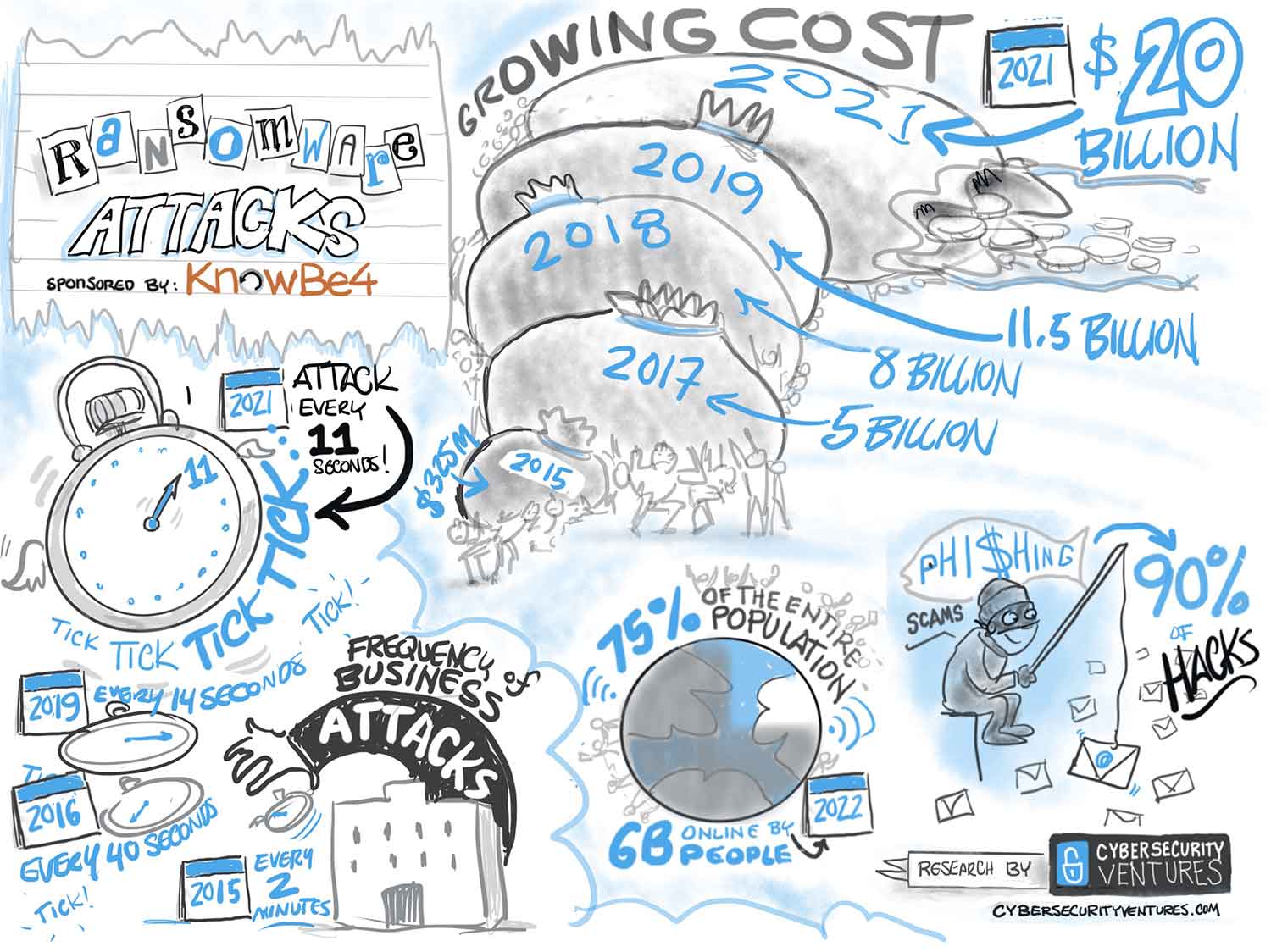
19 Oct Global Ransomware Damage Costs Predicted To Reach $20 Billion (USD) By 2021
Ransomware is expected to attack a business every 11 seconds by the end of 2021
 – Steve Morgan, Editor-in-Chief
– Steve Morgan, Editor-in-Chief
Northport, N.Y. – Oct. 21, 2019
Ransomware — a malware that infects computers (and mobile devices) and restricts their access to files, often threatening permanent data destruction unless a ransom is paid — has reached epidemic proportions globally and is the “go-to method of attack” for cybercriminals.
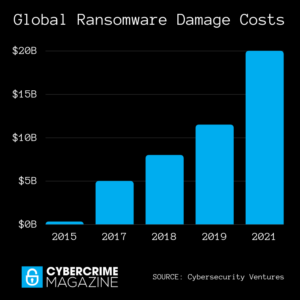
A 2017 report from Cybersecurity Ventures predicted ransomware damages would cost the world $5 billion in 2017, up from $325 million in 2015 — a 15X increase in just two years. The damages for 2018 were predicted to reach $8 billion, and for 2019 the figure is $11.5 billion.
The latest prediction is that global ransomware damage costs will reach $20 billion by 2021 – which is 57X more than it was in 2015. This makes ransomware the fastest growing type of cybercrime.
The 2015 to 2019 ransomware damage cost predictions have been corroborated by media outlets, academia, industry experts, numerous cybersecurity firms, and cybercrime fighters globally.
“Ransomware attacks are in the process of morphing from spray-and-pray phishing blasts to highly targeted and extremely damaging network-wide infections that can cause days or weeks of downtime for a whole organization,” says Stu Sjouwerman, founder and CEO at KnowBe4, a company that specializes in training employees on how to detect and respond to ransomware attacks. “It is an unfortunate fact of life that ransomware is here to stay and that traditional software-based endpoint protection is not able to protect well against this type of malware.”
It was estimated that every 40 seconds a business falls victim to a ransomware attack, in a December 2016 security bulletin posted by the cybersecurity firm Kaspersky Lab, which stated that the number of attacks rose from every two minutes in early 2016.
The big myth around ransomware damages is that the costs are limited to ransom payouts. However, the percentage of businesses and individuals who are paying bitcoin to reclaim access to their data and systems in response to ransom demands is declining (even if the total payout figures are rising due to the sheer volume of new attacks).
Ransomware costs include damage and destruction (or loss) of data, downtime, lost productivity, post-attack disruption to the normal course of business, forensic investigation, restoration and deletion of hostage data and systems, reputational harm, and employee training in direct response to the ransomware attacks. The estimations take attacks on businesses and individuals into consideration, and also include global ransom payouts.
CIOs, CISOs (Chief Information Security Officers), and IT security teams need to heighten their awareness and response plans around the ransomware threat. Cyber defense needs to cross boundaries so that every IT worker understands exactly what ransomware is, how it infects organizations, and how to combat it.
“Ransomware still uses social engineering as its main infection vector,” says KnowBe4’s Sjouwerman.
Training employees how to recognize and defend against cyber attacks (including phishing simulation programs to maximize the effectiveness of training) is the most under spent sector of the cybersecurity industry — and yet it holds out the greatest hope for combating ransomware attacks.
91 percent of cyberattacks begin with spear-phishing email, which are commonly used to infect organizations with ransomware.
Educating the world’s online population of 3.8 billion people — which is projected to reach 6 billion people by 2022 — on how to spot and react to spear-phishing emails is the next best thing to giving them ransomware vaccinations.
Cybersecurity Ventures predicts cybercrime will cost the world in excess of $6 trillion annually by 2021, up from $3 trillion in 2015. Ransomware is expected to worsen and make up a proportionately larger share of total cybercrime by 2021. Training employees is the big variable, and the potential big gainer in cutting down ransomware damage costs.
– Steve Morgan is founder and Editor-in-Chief at Cybersecurity Ventures.
Go here to read all of my blogs and articles covering cybersecurity. Go here to send me story tips, feedback and suggestions.